Many investors consider the foreign exchange market (also referred to as Forex or FX) to be one of the most intriguing and exciting markets in the world. The foreign currency market is an extensive subject; and too vast to cover in one article. Today we will cover the basic elements of the Forex, and some important considerations for traders to be aware of before deciding if the currency market is suited for their own trading style and risk tolerance.
What is the Forex?
The foreign exchange market is where currencies from all over the world are traded. The trading of foreign currencies is a necessity, as an exchange must occur between two countries in order to conduct business.
As an example, let's say a Swiss tourist was travelling in Peru and wanted to visit the historic ruins of Machu Picchu. The tourist is unable to use his Swiss francs for the entrance fee because it is not the local currency in Peru. He must exchange his Swiss francs for the Peruvian Sol (PEN), at the current exchange rate in order to visit the ruins.
In another example, you live in the USA and want to purchase wine from Portugal, which you order from your local wine retailer. The importer the store purchases the wine from will likely need to exchange the equivalent of US Dollars (USD) into Euros (EUR) in order to purchase the wine for you.
Because the need to exchange currencies around the globe is so great, the Forex market is considered to be the most liquid and largest financial market in the world. Comparing the Forex market with the stock market illustrates the magnitude of the Forex market. According to the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), the average daily volume of the Forex market at the end of 2017 was just over $5 trillion, changing constantly as more and more currencies are traded. The stock market is dwarfed in comparison, with an average daily volume of $55 billion on 6/29/18, as reported by the NYSE (New York Stock Exchange). One trillion equals 1,000 billion, so you can see the magnitude of the size of the Forex market.
Understanding how currencies are quoted can be confusing at first …
When a currency is quoted in the Forex market, it is always done in relation to another currency; the value of one currency is reflected through the value of another. This is called a currency “pair”. The USD/CHF is an example of a currency pair. The currency to the left of the slash (USD or US Dollar) is the base currency, and the currency on the right of the slash (CHF or Swiss Franc) is the counter currency, or quoted currency. The base currency is always equal to one unit. Therefore, if you wanted to determine the exchange rate between the US Dollar (USD) and the Swiss Franc (CHF), the Forex quote would look like this: USD/CHF = .9899.
There are two ways a currency pair is quoted; direct or indirect. A direct currency quote is a currency pair in which the domestic currency is the quoted currency. An indirect quote is a currency pair where the domestic currency is the base currency. So, if you were looking at the Swiss Franc (CHF) as the domestic currency and the US Dollar as the foreign currency, a direct quote would be USD/CHF, meaning that US $1 will purchase .9899 CHF. In this same example, an indirect quote would be the inverse (1 divided by .9989), 1.01 CHF/USD. This means with $1 Swiss Franc, you can purchase $1.01 US Dollars.
Most currencies are traded against the US Dollar, so in the majority of countries the US Dollar is the base currency, or a direct quote. However, this is not the case in currencies referred to as the Queen's currencies, or those that have or have had a tie with Great Britain. Examples of these include the New Zealand dollar (NZD), Australian dollar (AUD), as well as the Euro (EUR). In these cases, the US Dollar is the counter (quoted) currency, so it is referred to as an indirect quote.
What is a Cross Currency?
There is yet another term to become familiar with when learning the Forex language, and that is a cross currency. A cross currency is when a quote is given that does not include the US Dollar as one of its elements. Some common cross currency pairs include the EUR/CHF, EUR/GPB, and EUR/JPY. They present additional trading opportunities, but they are not as widely traded as pairs that include the US Dollar, referred to as the “majors”.
We'll cover more about pricing … bid/ask, spreads, etc., in a future article, but for now you have the basic language that is used in the Forex trading world on how currencies are quoted.
What are some of the advantages of trading the Forex market?
- While there are thousands of instruments traded in the equities market, the majority of those who trade the Forex market focus on seven different currency pairs. These include:
1) EUR/USD
2) USD/JPY
3) USD/CHF
4) GBP/USD
5) USD/CAD
6) AUD/USD
7) NZD/USD
These seven are considered to be the “majors”, and all other pairs are different combinations of the same currencies, called “cross currencies”, as explained above. This can make trading currencies easier to follow. Rather than following thousands of stocks, indices, or ETFs, Forex traders only need to stay abreast of the economic and political news of the countries in the major currency pairs.
- The currency market is open for trading 24 hours a day, 5-1/2 days per week. Market hours are from 5:00 PM ET Sunday through 5:00 PM ET Friday. This can be advantageous for traders who have a job during the day. As you can see from the chart below, the major currency hubs are spread across many different time zones. Some currency markets are open before the opening bell in the United States, while others open as the US markets close.
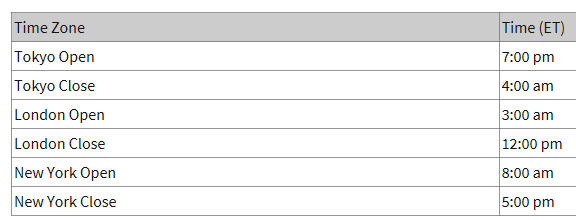
Figure A. Forex Market Time Chart (courtesy of Investopedia)
- The Forex market has much more liquidity than the equity market, which can make it easier to enter and exit positions.
- Commissions can sometimes be much lower in the Forex market than the equity market. Most Forex brokers create their profit from the spreads between the currencies.
- Because of the high liquidity in the Forex market, margins are lower than the equity market. Most brokers in the equities market require at least 50% of the value of the investment for margin. In comparison, Forex brokers can require as little as 1%.
- A Forex trader has the ability to choose various levels of leverage. This allows the trader to choose the risk/reward that fits their comfort level.
Is there a downside of trading in the Forex market?
The high leverage available to traders in the Forex market can be a double-edged sword, and brings a higher risk in comparison to trading equities. This high leverage means that any gains can quickly turn into major losses in a matter of minutes.
What is leverage? “Leveraged investing is a technique that seeks higher investment profits by using borrowed money. These profits come from the difference between the investment returns on the borrowed capital and the cost of the associated interest. Leveraged investing exposes an investor to higher risk” according to Investopedia.com.
While currencies normally don't move as dramatically as equities on a percentage basis, it is the leverage in the Forex market that creates the volatility. For example, if you are using 50:1 leverage on a $1,000 investment, you control $50,000 of capital. If you invest $50,000 into a particular currency and that currency's price moves 1% against you, the value of that capital has decreased to $49,500 – a loss of $500. This loss represents 50% of your investment.
Compare this to the equities market, where most traders do not use leverage… Using the same example of investing $1,000 into a particular stock: If that stock price drops 1%, the loss incurred would only be $10, 1% of your investment. It is critical that traders be aware of the risk of leverage before diving into the Forex market.
In conclusion …
Trading the Forex market can be an exciting and diverse addition to a trader's tool box. The liquidity of currencies, and being able to trade outside the US market hours, has its advantages. However, as with any instrument or trading strategy, trading the Forex market comes with risks associated with the benefits. Be sure you have a complete understanding of all the risks and the potential effect they can have on your trading capital before investing in the currency market.
This introductory article barely scratches the surface of the vast Forex market. Future articles will cover more specifics of trading the foreign currency market such as bid/ask pricing, spreads, and pips.
If you trade currencies and have any experiences you would like to share to subscribers, feel free to comment below.
Are you new to trading looking for mentoring, or an educational trade alert service? Or, are you a veteran seeking a trading group where you can interact with like-minded traders who share their experiences? Look no more. Join Aeromir today!


